- Myopia,
- Hypermetropia
- Presbyopia
- Astigmatism
MYOPIA (Nearsightedness)
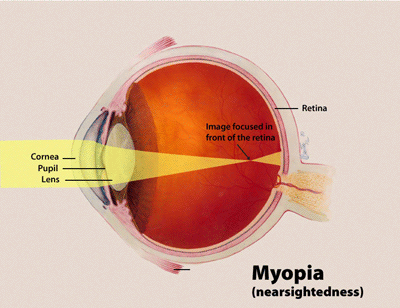
- A person sees near objects clearly while distant objects appear blurred.
- In such a defective eye, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina itself.
CAUSES:
This defect arises because the power of the eye is too great due to the decrease in focal length of the crystalline lens.
This may arise due to either
- excessive curvature of the cornea, or
- elongation of the eyeball.
CORRECTION :
- This defect can be corrected by using a concave (diverging) lens.
- A concave lens of appropriate power or focal length is able to bring the image of the object back on the retina itself.
HYPERMETROPIA (Farsightedness)
- A person sees near objects with blurred vision, while distant objects appear in sharp focus.
- In this case, the image is formed behind the retina.
CAUSES:
This defect arises because either
- The focal length of the eyelens is too great, or
- The eyeball becomes too short, so that light rays from the nearby object, say at point N, cannot be brought to focus on the retina to give a distinct image.
CORRECTION :

This defect can be corrected by using a convex (converging) lens
of appropriate focal length. When the object is at N’, the eye exerts
its maximum power of accommodation. Eyeglasses with converging lenses
supply the additional focussing power required for forming the image on
the retina.
PRESBYOPIA:

- Presbyopia, progressive form of farsightedness that affects most people by their early 60s.
- The power of accommodation of the eye decreases with ageing.
- Most people find that the near point gradually recedes.
CAUSES AND CURE:
- It arises due to the gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the crystalline lens.
- Simple reading eyeglasses with convex lenses correct most cases of presbyopia. Sometimes, a person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia. Such people often require bi-focal lenses.
BI-FOCAL LENSE-> The
upper portion of the bi-focal lens is a concave lens, used for distant
vision. The lower part of the bi-focal lens is a convex lens, used for
reading purposes.
ASTIGMATISM

- Astigmatism, a defect in the outer curvature on the surface of the eye that causes distorted vision.
- a person cannot simultaneously focus on both horizontal and vertical lines.
CAUSES:
- This defect is usually due to the cornea that is not perfectly spherical.
- Consequently, it has different curvatures in different directions in vertical and horizontal planes.
- This results in objects in one direction being well-focussed, while those in a perpendicular direction not wellfocussed.
CORRECTION :

Post a Comment
Post a Comment